-
Written by Dr.Mehmet Demircioglu
- Estimated Reading Time 4 Minutes
Unshaven Hair Transplants: Discreet Approach to Hair Restoration
What Is Unshaven Hair Transplant?
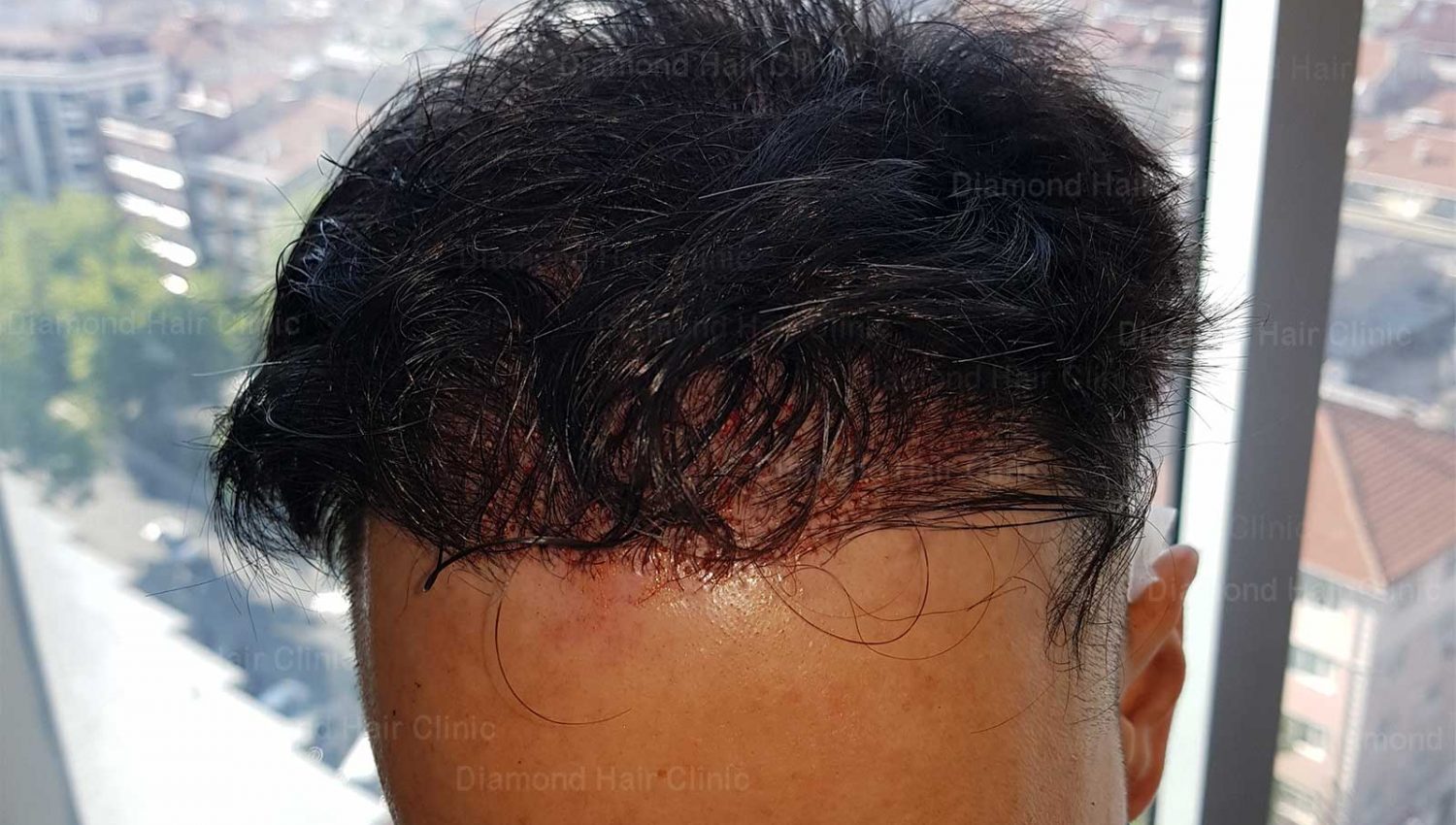
“Unshaven Hair Transplant” (U-FUE) is a highly specialized, discreet form of hair restoration surgery that bypasses the conventional requirement of cutting or shaving the donor and/or recipient areas on the scalp.
Originating from advancements in the early 2010s, this method has seen various improvements to tackle its specific obstacles. Designed to render both the surgical phase and post-surgery recovery less noticeable, this approach serves individuals keen on preserving their natural look during the entire surgical process. Particularly attractive to people in professional roles and public personalities, “Unshaven Hair Transplant” is intended for those desiring a continuous natural aesthetic throughout the surgical procedure.
Moreover, advancements in hair transplantation techniques have led to minimally invasive, scar-free, and natural-looking results [Gupta et al., 2015, Journal of Cutaneous Medicine and Surgery].
The unshaven hair transplant widely leverages up-to-date hair transplant methodologies such as Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE) or Direct Hair Implantation (DHI).
Despite its aesthetic advantages, the unshaven approach presents logistical and operational challenges for the medical team and hair restoration surgeon. Specifically, the absence of shaving can compromise visibility, increase the complexity of the operation, and extend procedure times by %25-30.
Hair length and quality, as well as surgery time, are also cited as challenges, especially when dealing with patients who have inadequate head donor supply [Umar, 2011, Annals of Plastic Surgery].
These challenges demand superior skill and experience from the surgical team to ensure accurate follicle extraction and optimal placement during implantation. Moreover, due to reduced operational clarity and maneuverability, the method may introduce higher risks of complications such as graft dislodgment or infection.
Hair transplantation has a general complication rate of 4.7% in a series of 533 procedures, with enlarged scar, folliculitis, and necrosis being the most common complications [Salanitri et al., 2009, Aesthetic Surgery Journal].
Surgeons should be aware of possible complications and techniques for prevention and management, as complications may impact the social and psychological aspects of the patient [Kerure & Patwardhan, 2018, Journal of Cutaneous and Aesthetic Surgery].
The most serious complication of hair transplantation is necrosis [Küçüktaş, 2017].
An unshaven hair transplant is a niche yet aesthetically appealing option to provide a more discreet surgical experience. However, the complexities may affect the overall efficacy and safety of the transplantation procedure.
Key Takeaways
- Unshaven Hair Transplant (U-FUE) is a specialized form of hair restoration that eliminates the need for shaving, targeting a discreet surgical experience.
- Initially developed in the early 2010s, U-FUE attracts professionals and public figures who want to maintain a natural look throughout the procedure.
- The technique integrates well with advanced hair transplant methods like FUE and DHI.
- While offering aesthetic benefits, U-FUE increases the procedure time and complexity by 25-30%.
- Surgeons need advanced skills to navigate the operational challenges presented by U-FUE, such as reduced visibility.
- U-FUE appeals to both men and women but for different societal and aesthetic reasons.
- Variants of U-FUE exist to cater to diverse patient needs and levels of hair loss.
- The procedure is generally 40-50% more expensive than traditional methods due to its complexity and time requirements.
- Dr. Mehmet Demircioglu often discourages U-FUE, citing its elevated risks and complexities, especially for those with extensive hair loss.
The Fundamentals of Unshaven Hair Transplant
What Exactly is an Unshaven Hair Transplant?
An Unshaven Hair Transplant is a variation of standard hair transplant techniques like Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE) or Direct Hair Implantation (DHI). The unique feature of this method is the retention of existing hair length in both the donor and recipient areas, aiming for a less noticeable post-operative appearance.
How Does It Differ From Traditional Hair Transplant Methods?
The core difference lies in the preparatory steps. Traditional methods require shaving the hair to give the surgeon a clear view of the scalp, facilitating easier extraction and implantation of hair follicles. In contrast, “Unshaven Hair Transplant” maintains the existing hair, a natural camouflage during the healing phase, but also introduces particular challenges.
What Methods Are Utilized In Unshaven Hair Transplant?
In unshaven hair transplants, two primary techniques come into play: Manual FUE for graft extraction from the donor area and the DHI Pen for placing these grafts into the recipient zone. In the Manual FUE stage, a hand-operated micro punch tool makes tiny perforations less than 1 mm in size in the donor area for harvesting grafts. These follicular units are then prepped for transplantation. In the subsequent implantation phase, a specialized instrument known as the Choi Pen, or DHI Pen, is employed, eliminating the necessity for incisions in the recipient area’s scalp.
Why Shaving Is Critical Before Hair Transplant Procedure?
Shaving both the donor and receiver areas before a hair transplant is a vital step toward the success and satisfactory results of the surgery. Not shaving could limit the number of grafts to a maximum of 1000-1500 follicular units. It could also interfere with hair regrowth and potentially jeopardize the ultimate result of the transplant. Shaving hair is not just a formality, it plays a key part in maintaining a sterile surgical environment on the scalp, improving precision, and boosting the procedure’s success rate. In addition, it ensures a safer and higher quality post-operative phase.
Challenges and Risks
While “Unshaven Hair Transplant” has aesthetic advantages, it presents several operational challenges:
- Visibility and Complexity: The unshaven hair can obstruct the surgeon’s view, making extraction and implantation more challenging.
- Operational Time: Due to these complexities, the time required for “Unshaven Hair Transplant” is generally 25-30% longer than traditional methods. S. Umar’s study (2011) in the Annals of Plastic Surgery also highlights that surgery time remains a challenge in hair transplantation.
- Skill Requirement: The procedure requires a surgical team with advanced skills in hair restoration techniques.
- Risk of Complications: Reduced visibility can lead to higher graft dislodgment or bacterial infection risks. This is supported by a study by A. Kerure and Narendra Patwardhan, published in the Journal of Cutaneous and Aesthetic Surgery in 2018, which states that proper surgical technique and wound care are crucial for minimizing complications.
Eligibility Criteria for Unshaven Hair Transplant
Patient Suitability: Not a One-Size-Fits-All Solution
Non-shaven hair transplants are not a one-size-fits-all solution for everyone. The determining factors for suitability include:
– The patient’s hair characteristics
A study by Seonsik Yun et al., published in the Archives of Plastic Surgery in 2017, emphasizes that hair diameter varies significantly in different vertical sections of the occipital safe donor area, making it crucial for planning hair transplant surgery.
– The pattern and extent of hair loss
– Patient health conditions
For instance, individuals with diffuse thinning may face an increased risk of transection, a complication where neighboring hair follicles are inadvertently cut during the procedure, potentially leading to permanent surgical damage or hair loss.
Who Makes an Ideal Candidate?
The ideal candidate typically:
- Mild Hair Loss or Early Stage Receding Hairline: The optimal candidates for no-shave hair transplant typically require less than 2,000 grafts. These individuals are usually at the Norwood Stage 1-3 or experiencing hair loss solely in the Crown Area. A no-shave hair transplant offers a specific solution for those in the early stages of hair loss.
- Patients With Long Hair Who Wish To Keep the Procedure Discreet: The no-shave hair transplant is suitable for both men and women with hair exceeding 6-7 cm in length, as it allows the concealment of the extraction site at the back of the head.
- Good Health: Patients who are generally in good health to reduce post-operative complications.
Gender Considerations
Women often find “Unshaven Hair Transplant” more appealing due to societal norms and personal preferences about hair length.
A study by W. Unger and R. Unger, published in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology in 2003, suggests that hair transplanting should be considered as a potential treatment option for most women with pattern hair loss.
Men, too, opt for this if they wish to keep their hair restoration private.
Who Should Avoid It?
People with extensive or severe hair loss are generally not candidates for an “Unshaven Hair Transplant.” The method’s limitations become more pronounced when many grafts are required.
Variants of Unshaven Hair Transplant
Unshaven Hair Transplant itself has different variants depending on the patient’s needs and the extent of hair loss:
- Unshaven Recipient Area, Limited Shaven Donor Area: Only a tiny portion of the donor area is shaved, making hiding easier.
- Unshaven Recipient Area, Shaven Donor Area: Suitable when the recipient area is completely bald.
- Unshaven Recipient Area, Unshaven Donor Area: Neither the donor nor the recipient area is shaved. This is the most discreet but also the most complex variant.
Potential Risks and Complications of Non-Shaven Hair Transplants
- Incomplete Camouflage: Since the surrounding hair is not shaved, it may be challenging for the surgeon to blend the newly transplanted hair with the existing hair seamlessly. This could result in a less natural appearance, mainly if hair density varies across the treated area. A study by S. Hwang et al., published in Dermatologic Surgery in 2009, suggests that the recipient site influences the growth characteristics of transplanted hairs.
- Higher Risk of Infection: Non-shaven hair transplants may have a slightly increased risk for infections, as the existing hair can make maintaining an utterly sterile environment during the procedure challenging. Proper postoperative care and adherence to the surgeon’s instructions can help mitigate this risk.
- Prolonged Healing Time: Existing hair can make keeping the transplant site clean challenging, potentially leading to inflammation and prolonged healing time. Patients should follow all postoperative care instructions closely to ensure optimal healing.
- Increased Risk of Graft Damage: Non-shaven hair transplant requires more skill and precision from the surgeon during extraction and implantation. If not performed carefully, there is an increased risk of damaging the hair grafts, which could affect the overall success of the transplant.
- Increased Transection Rate: The risk of accidentally cutting neighboring follicles during the procedure, particularly in recipient area incisions, potentially leading to permanent surgical damage or hair loss. A study by E. Raposio et al., published in Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery in 1998, suggests that the in vitro survival rate of transected human hair follicles might represent an interesting starting point in striving to augment the number of donor hairs available during a hair transplantation procedure.
- Inaccurate Graft Placement: The surrounding hair can obstruct the surgeon’s view during implantation, making it more challenging to place the grafts accurately. Misplaced grafts may result in an unsatisfactory appearance, requiring additional procedures to correct the issue.
- Shock Loss Post-Hair Transplant: Regardless of the specific technique used for hair transplantation, the risk of post-surgical shock loss exists. This hair loss is induced by scalp trauma and can affect the transplant site and the donor area. When considering unshaved hair transplants, it’s important to note that longer, unshaved hair is also susceptible to shock loss, potentially diminishing the advantages of opting for a no-shave procedure.
Disadvantages and Limitations
- Time-Consuming: The procedure takes longer due to its complexity.
- Skill Dependency: Success largely depends on the skill of the surgical team.
- Cost Implications: The cost of a no-shave hair transplant procedure is generally %40-50 more expensive than traditional methods due to the required extended operational time and skill.
- Post-Operative Care: Due to the complexities introduced by the presence of existing hair, post-operative care can be more challenging.
Get an Expert Opinion Before Deciding Non-Shave Hair Transplant
Numerous vital aspects should be evaluated before selecting an Unshaven Hair Transplant. The optimal approach involves consulting a hair transplant surgeon. An in-depth discussion with a hair restoration expert is essential for a precise evaluation.
According to a study published in the Aesthetic Surgery Journal in 2009 by Salanitri et al., the challenges in hair transplantation generally include the need for good communication between patient and surgeon, accurate surgical technique, specific equipment, and a trained surgical team.
Why Does Dr. Mehmet Demircioglu in Diamond Hair Clinic Advise Against No-Shave Hair Transplants?
While conducting a hair transplant without shaving the recipient area is feasible, Dr. Mehmet Demircioglu often dissuades patients from “No-Shave Hair Transplant” approach. The drawbacks, such as suboptimal results and potential harm to the grafts, generally outweigh the short-term benefits, especially for those with extensive baldness.
Get In Touch With Diamond Hair Clinic!
- Dr. Mehmet Demircioglu is an experienced and qualified hair transplant surgeon who founded Diamond Hair Clinic, one of Turkey’s best hair restoration clinics.
- Contact us to schedule a free consultation.